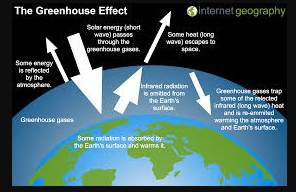
Whether or not you believe the greenhouse effect is actually real, the truth is that it is very important to understand and take advantage of. By learning how it works, you will be able to better protect yourself and your family.
Cloud cover
Despite their relative smallness, clouds play a key role in regulating Earth’s climate. They trap infrared radiation, reflect sunlight back into space, and slow down the rate of surface cooling.
The effect of clouds on the climate may be both positive and negative. For example, a reduction in cloud cover may increase the amount of available solar flux in the lower atmosphere, which may lead to a warming effect. On the other hand, a change in cloud cover may also dampen the effect of climate change.
A number of studies have examined the relationship between clouds and climate. Some of these studies have used computer models to model the effects of clouds on climate. Others have used real-world observations to analyze the effects of cloud cover on climate.
Fossil fuels
During the last 150 years, fossil fuels have been a major source of energy. They have been used to power industries, transport goods, and provide electricity. They are also the largest contributing cause of climate change.
Fossil fuels are natural resources that contain a lot of carbon and hydrogen. These gases are trapped in rock layers and are released when fossil fuels are burned. Depending on their carbon content, the amount of CO 2 released can vary greatly.
Fossil fuels are formed millions of years ago from the decomposition of plants and animals that died 540 million to 65 million years ago. They are deposited in cracks and pores of sedimentary rock. They are also present in tar sands near the earth’s surface.
Fossil fuels provide about 80% of the world’s energy. However, the supply is limited. As a result, the supply will gradually decline.
Water vapor
Increasing the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere is one of the most effective ways to increase the greenhouse effect. Increased atmospheric water vapor will cause more water to evaporate and the resulting increase in surface temperature will also increase the greenhouse effect.
The water vapor greenhouse effect is a major contributor to Earth’s overall temperature change. It has been estimated that water vapor accounts for approximately 70% of the total greenhouse effect. During the past two decades, large increases in temperature and humidity have been observed in central Europe. The resulting warmer air can hold more water and will therefore increase precipitation and drought.
Water vapor is an effective greenhouse gas because it traps the incoming longwave radiation from the earth’s surface. As a result, it increases the total greenhouse effect by adding an additional 1.86 W m of radiative forcing for every one degree of surface warming.
Plants
Using a greenhouse is a common method for growing plants. Greenhouses are houselike structures built out of glass or plastic. The greenhouses protect plants from cold and other adverse weather conditions.
The greenhouse concept was first developed in the Netherlands in the 17th century. Its main purpose is to provide a regulated environment for growing crops.
Plants in the greenhouse effect absorb gases from the atmosphere and convert them to food. This occurs during photosynthesis. The greenhouse environment allows plants to grow in a favourable micro-climate that favours crop production year round.
The temperature of the interior of a greenhouse can be regulated with simple techniques. Exhaust fans with thermostats are used to control the temperature. The use of insulating screens and shading materials can reduce the light intensity in the greenhouse.
Sun’s radiations
Getting a glimpse of the sun’s radiations is a crucial part of understanding the greenhouse effect. It helps to understand how the energy that comes from the sun is transformed into energy that is absorbed or reflected by the atmosphere.
The radiation from the sun is primarily in the form of short-wave and long-wave radiation. The short-wave radiation is visible and easily passes through the atmosphere, while the long-wave radiation is infrared.
In addition to these, the sun’s radiations are also reflected by the outer atmosphere. About 30% of the incoming radiation is reflected back to space. The absorbed energy is then reradiated back to space. In addition to the long-wave radiation, the Earth is also a black body, which is a term used to describe the sun’s energy. This radiation has a wavelength of longer than 288 K, which is slightly cooler than the average surface temperature on Earth